Extreme Quantum Matter Physics RIKEN ECL Research Unit
Principal Investigator
- PI Name
- Yukako Fujishiro
- Title
- RIKEN ECL Unit Leader
- HP
- https://sites.google.com/view/yukako-fujishiro/home?authuser=0
- Brief Resume
2021 D. Eng., The University of Tokyo 2021 Special Postdoctoral Researcher, RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science 2024 RIKEN ECL Unit Leader, Extreme Quantum Matter Physics RIKEN ECL Research Unit, Cross-Divisional Materials Research Program, RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (–present) 2024 RIKEN ECL Unit Leader, Extreme Quantum Matter Physics RIKEN ECL Research Unit, RIKEN Cluster for Pioneering Research (–present) 2025 RIKEN ECL Unit Leader, Extreme Quantum Matter Physics RIKEN ECL Research Unit, RIKEN Pioneering Research Institute (–present)

Outline

In our unit, we aim to investigate intriguing emergent phenomena in magnetic topological materials and strongly correlated electron system, with a particular emphasis on “extreme” conditions previously unattainable in earlier experiments. For instance, we employ microfabrication techniques on single crystalline quantum materials using focused ion beams (FIB). This enables us to (i) perform precise magneto-transport study under ultra-high pressure, (ii) explore magnetization dynamics in spin textures under high-density currents, and (iii) manipulate carrier densities in bulk layered materials through ion intercalation. Through these innovative approaches, we aim to reveal new quantum phases and elucidate their electronic functionalities.
Research Fields
Physics, Engineering, Materials Sciences
Keywords
Magnetic topological material
Strongly correlated electron system
Charge transport phenomena
Itercalation
Ultra-high pressure
Results
Ultra-high-pressure control of strongly correlated electron system
In strongly correlated electron systems, the conventional band picture breaks down under strong electron-electron interactions, giving rise to a variety of electronic phases such as Mott insulators and high-temperature superconductors. If we could freely control these interactions, it would open the door to new quantum phases and functionalities. We applied extremely high pressure to the half-filled, quasi-one-dimensional Mott insulator K-TCNQ and observed a transition from a Mott insulator with a spin-Peierls state to a charge-ordered phase. While this behavior aligns with the one-dimensional extended Hubbard model, it has never been experimentally confirmed. Furthermore, we discovered a novel ground state—referred to here as a “quantum dimer liquid”—in which dimer fluctuations persist even at the lowest temperatures. These findings were achieved through electrical resistivity measurements under high pressure using a diamond anvil cell, synchrotron X-ray diffraction, optical measurements, and collaborative research involving first-principles calculations. Going forward, we will continue to combine multifaceted experiments and theoretical analyses to explore the uncharted quantum phases hidden in strongly correlated electron systems.
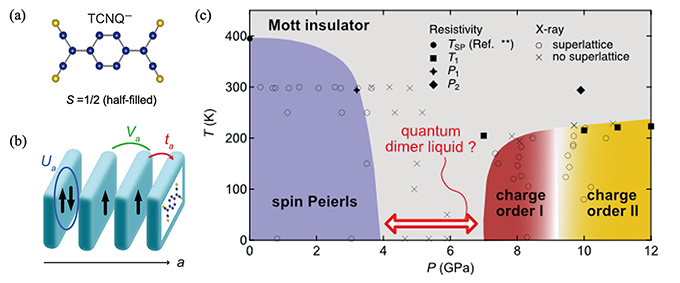
(a) Chemical formula of TCNQ. (b) Schematic view of a TCNQ chain with on-site (Ua) and inter-site (Va) Coulomb interaction and transfer integral (ta). (c) Pressure-temperature phase diagram of K-TCNQ consisting of spin-Peierls and two distinct charge ordered states, along with the possible quantum dimer liquid.
Topological magnetic phase transitions explored under ultra-high pressure
Investigating new quantum phases stands as a pivotal subject in condensed matter physics. Specifically, the quantum phase transition, characterized by the suppression of long-range magnetic order at zero-temperature, reveals a variety of novel quantum phase. These include non-Fermi liquid states, high-temperature superconductivity driven by antiferromagnetic fluctuations, and unconventional superconductivity mediated by ferromagnetic fluctuations.
In this research, we focused on the quantum phase transition of helical spin textures and magnetic skyrmions. We applied ultra-high pressure (~50 GPa) in a chiral magnet FeGe and unveiled an exotic quantum phase. In specific, we observed a metal-to-insulator transition induced by dramatic changes in the band structure, as well as the emergence of spontaneous anomalous Hall effect induced by the short-range magnetic order above the quantum phase transition. This unconventional anomalous Hall effect, which cannot be explained by conventional mechanisms, seems to be related to the quantum fluctuations in chiral systems.
Experimentally, the precise magneto-transport study under ultra-high pressure was enabled by our innovative technique using FIB method. We anticipate that this method will significantly contribute to the discovery of new quantum phases in the high-pressure regime.
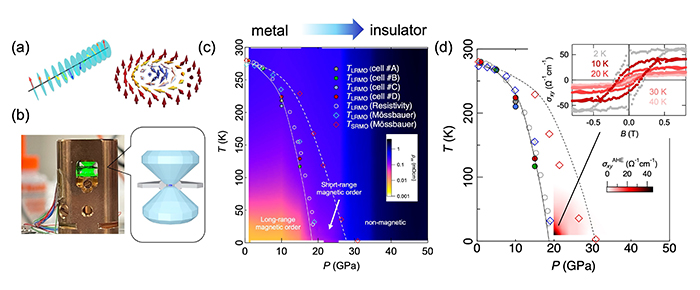
(a) Schematic illustration of helical spin texture and magnetic skyrmion in a chiral magnet FeGe. (b) Optical picture and schematic illustration of diamond anvil cell used in the experiment. (c) Contour map of resistivity in the temperature-pressure phase diagram. (d) Contour map of Hall conductivity of the unconventional spontaneous anomalous Hall effect enhanced around the quantum phase transition.
Members
| Yukako Fujishiro | RIKEN ECL Unit Leader | yukako.fujishiro[at]riken.jp | |
|---|---|---|---|
Misaki Sasaki |
Research Associate | ||
Yuri Suzuki |
Student Trainee |
Publications
- Y. Fujishiro, C. Terakura, A. Miyake, N. Kanazawa, K. Nakazawa, N. Ogawa, H. Kadobayashi, S. Kawaguchi, T. Kagayama, M. Tokunaga, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, K. Shimizu , and Y. Tokura
Phys. Rev. B 110, L220401 (2024)Pressure-induced quantum melting of chiral spin order and subsequent transition to a degenerate semiconductor state in FeGe
- D. Singh, Y. Fujishiro, S. Hayami, S. H. Moody, T. Nomoto, P. R. Baral, V. Ukleev, R. Cubitt, N.-J. Steinke, D. J. Gawryluk, E. Pomjakushina, Y. Onuki, R. Arita, Y. Tokura, N. Kanazawa, and J. S. White
Nat. Commun. 14, 8050 (2023)Transition between distinct hybrid skyrmion textures through their hexagonal-to-square crystal transformation in a polar magnet
- Y. Fujishiro, N. Kanazawa, R. Kurihara, H. Ishizuka, T. Hori, F. S. Yasin, X.Z. Yu, A. Tsukazaki, M. Ichikawa, M. Kawasaki, N. Nagaosa, M. Tokunaga, and Y. Tokura
Nat. Commun. 12, 317 (2021)Giant anomalous Hall effect from spin-chirality scattering in a chiral magnet
- M. Tanaka, Y. Fujishiro, M. Mogi, Y. Kaneko, T. Yokosawa, N. Kanazawa, S. Minami, T. Koretsune, R. Arita, S. Tarucha, M. Yamamoto, and Y. Tokura
Nano Lett. 20, 7476-7481 (2020)Topological Kagome Magnet Co3Sn2S2 Thin Flakes with High Electron Mobility and Large Anomalous Hall Effect
- Y. Fujishiro, N. Kanazawa, and Y. Tokura
Appl. Phys. Lett. 116, 090501 (2020)Engineering skyrmions and emergent monopoles in topological spin crystals
- Y. Fujishiro, N. Kanazawa, T. Nakajima, X. Z. Yu, K. Ohishi, Y. Kawamura, K. Kakurai, T. Arima, H. Mitamura, A. Miyake, K. Akiba, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, T. Koretsune, R. Arita, and Y. Tokura
Nat. Commun. 10, 1059 (2019)Topological transitions among skyrmion- and hedgehog-lattice states in cubic chiral magnets
- Y. Fujishiro, N. Kanazawa, T. Shimojima, A. Nakamura, K. Ishizaka, T. Koretsune, R. Arita, A. Miyake, H. Mitamura, K. Akiba, M. Tokunaga, J. Shiogai, S. Kimura, S. Awaji, A. Tsukazaki, A. Kikkawa, Y. Taguchi, and Y. Tokura
Nat. Commun. 9, 408 (2018)Large magneto-thermopower in MnGe with topological spin texture
Contact Us
2-1 Hirosawa, Wako 351-0198 Japan
E-mail:
yukako.fujishiro[at]riken.jp
